Fibrillary (Diffuse) Astrocytomas and Glioblastoma Multiforme
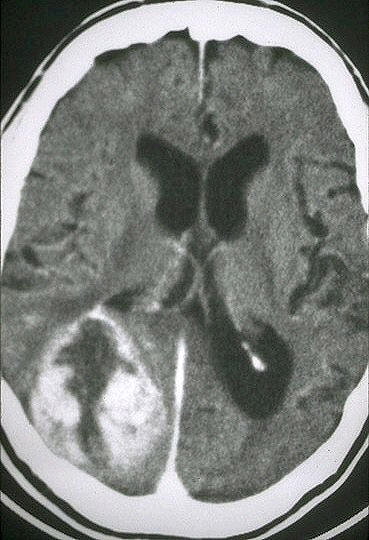
These account for
about 80% of adult primary brain tumors...
Astrocytomas are
supratentorial...got
to know this!!!
Usually
found in the cerebral hemispheres,
they may also occur in the cerebellum, brain stem, or spinal cord, most often in
the fourth through sixth decades...
The most common
presenting signs and symptoms are seizures,
headaches, and focal neurologic deficits related to the anatomic site
of involvement....
Fibrillary
astrocytomas show a spectrum of histologic differentiation that correlates well
with clinical course and outcome...
Mild to moderate increase in the number of glial cell
nuclei, somewhat variable nuclear pleomorphism,
and an intervening feltwork of fine, GFAP-positive astrocytic cell processes
that give the background a fibrillary appearance...
The transition
between neoplastic and normal tissue is indistinct, and tumor cells can be seen
infiltrating normal tissue at some distance from the main lesion...
Anaplastic
astrocytomas show regions that are more densely cellular and have greater
nuclear pleomorphism form well-differentiated fibrillary astrocytoma;
mitotically active cells or some vascular endothelial proliferation is also
observed...
When the predominant
neoplastic astrocyte shows a brightly eosinophilic cell body from which emanate
abundant, stout processes, the term genistocytic astrocytoma applies...
 Found
in cerebral hemispheres...most
common brain tumor...
Found
in cerebral hemispheres...most
common brain tumor...
Sudden
grand mal seizure...
Small
cells with elongated nuclei and bipolar processes are characteristic...
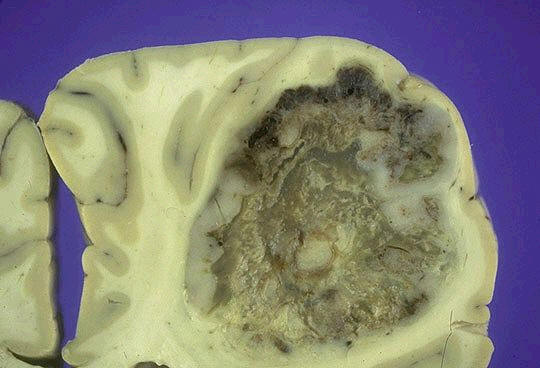
Glioblastoma
multiforme has a histologic appearance similar to anaplastic astrocytoma with
the additional features of necrosis
and vascular or endothelia cell proliferation - tufts of piled up vascular cells that bulge into the vascular lumen...
One of
the causes that must be considered with a high
CSF protein is a tumor
When vascular cell
proliferation is extreme, the tuft forms a ball-like structure, the glomeruloid
body...
Vascular endothelial
cell growth factor (VEGF), produced by malignant astrocytes, perhaps in response
to hypoxia, contributes to this distinctive form of vascular change...
Necrosis in
glioblastoma multiforme, often in a serpentine pattern, ocurs in areas of
hypercellularity with highly malignant
tumor cells crowded along the edges of the necrotic
regions, producing a histologic pattern referred to as
pseudopalisading...
In the condition
called gliomatosis cerebri multiple regions of the brain, in some cases, the
entire brain, are infiltrated by neoplastic astrocytes...
Astrocytomas

Clinical features
depend in part on the location of the lesion and its
rate of growth...
Astrocytomas have a
tendency to become more anaplastic with time...
With well
differentiated astrocytomas, the symptoms may remain static or progress only
slowly during a number of years...
Eventually, however,
patients usually enter a period of more rapid clinical deterioration that is
generally correlated with the appearance of anaplastic features and more rapid
growth of the tumor...
The prognosis for
patients with glioblastoma is very poor...
With current
treatment, comprising resection when feasible together with radiotherapy and
chemotherapy, the mean length of survival after diagnosis is only 8-10 months;
less than 10% of patients are alive after 2 years...
Survival is
substantially shorter in older patients...well-differentiated astrocytomas have
a mean survival of more than 5 years...
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
 They
behave benignly...
They
behave benignly...
Typically occur in
children and young adults
and are usually
located in the cerebellum
but may also appear in the floor and walls of the third ventricle, the optic
nerves, and occasionally the cerebral hemispheres...
Pilocytic
astrocytomas is often cystic, with a
mural nodule in the wall of the cyst; if solid, it may be well circumscribed or,
less frequently, infiltrative...
Microscopic
examination reveals the tumor is composed of bipolar cells with long, thin "hairlike" processes that are GFAP-positive;
Rosenthal fibers
and
microcysts are often present...
An increase in the
number of blood vessels, often with thickened walls, is seen but does not imply
an unfavorable prognosis; necrosis and mitoses are uncommon...
These tumors grow
very slowly, and some patients have survived for more than 40 years after
incomplete resection...
Oligodendroglioma
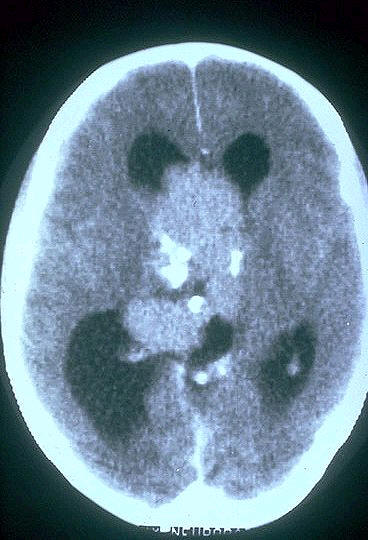
Most
often occurs in frontal lobes...
These tumors
constitute about 5-15% of gliomas and are most
common the fourth and fifth decades...
Patients may have had
several years of neurologic complaints, often
including seizures...
The lesions are found
mostly in the cerebral hemispheres, with a
predilection for white matter...
Macroscopicly they are well circumscribed, gelatinous, gray masses, often with
cysts, focal hemorrhage, and
calcificaiton...
"Fried
Egg"
appearance...
Microscopicly, the
tumor is composed of sheets of regular cells with
spherical nuclei containing finely granular chromatin (similar to
normal oligodendrocytes) surrounded by a clear halo
of cytoplasm...
The tumor typically
contains a delicate network of anastomosing
capillaries...
The
calcification,
which is present in as many as 90% of these tumors, ranges from microscopic foci
to massive depositions...
At present, no
diagnostically reliable immunohistochemical markers have been developed for
oligodendroglioma...
Patients with oligodendrogliomas have a better
prognosis than that of patients with astrocytomas...
Current treatement
with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy has yielded an average survival of
5 to 10 years...
Patients with
anaplastic oligodendroglioma have a worse prognosis...
The term mixed glioma
has been employed to designate neoplasms consisting of oligodendroglioma and
astorcytoma (or less often another gliomatous component)...
Ependymoma Tumors
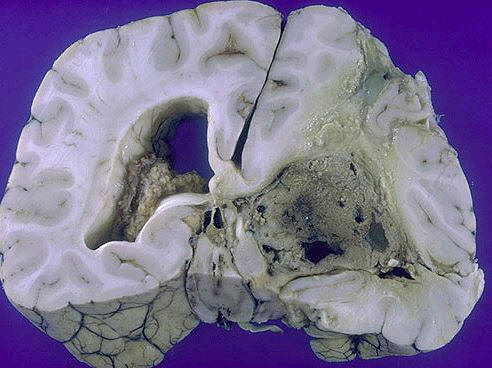 Ependymomas
most often arise next to the ependyma lined ventricular system, including the oft-obliterated central canal of the spinal
cord...
Ependymomas
most often arise next to the ependyma lined ventricular system, including the oft-obliterated central canal of the spinal
cord...
In the first two
decades of life, they typically occur near the fourth ventricle and constitute 5-10% of the primary brain tumors in
this age group...
In adults, the
spinal cord is the most common location...
The fourth ventricle, ependymomas are typically solid or papillary masses
extending from the floor of the ventricle...
Although they are
often better demarcated from adjacent brain than astrocytomas, their proximity
to the vital pontine and medullary nuclei usually makes complete extirpation impossible...
In the intraspinal
tumors, this sharp demarcation sometimes makes total removal feasible...
On microscopic
examination, ependymomas are composed of cells with
regular, round to oval nuclei with abundant granular chromatin...
Between the nuclei,
there is a variably dense fibrillary background...tumor
cellls may form glandlike round or elongated
structures
("rosettes," canals)that resemble
the embryologic ependymal canal with long, delicate processes extending into a
lumen; more frequently present are
perivascular pseudorosettes
in which tumor cells
are arrranged around vessels with an intervening zone consisting of then
ependymal processes directed toward the wall of the vessel...
About 50% of
ependymomas can be shown immunocytochemically to contain GFAP...most tumors are
well differentiated, but anaplastic forms also occur...
Posterior fossa ependymomas often manifest with
hydrocephalus secondary to progressive obstruction of the fourth ventricle
rather than invasion of the pons or medulla...
Prognosis is poor
despite the slow growth of the tumor and the usual lack of histologic evidence
of anaplasia...
B/C of their
relationship to the ventricular system, CSF dissemination is a common
finding....
An average survival
of about 4 years after surgery and radiotherapy has been reported...
Medulloblastoma
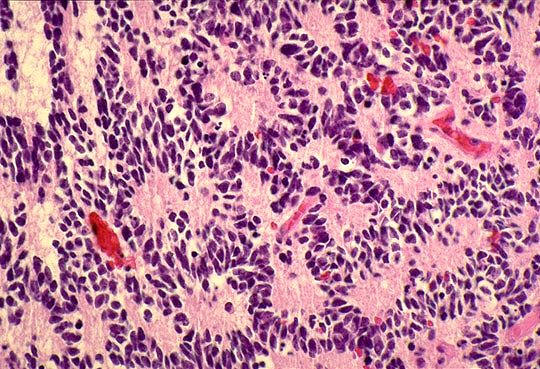
This tumor
occurs predominantly in children and
exclusively in the
cerebellum...
Neuronal and glial
markers may be expressed, but the tumor is often largely undifferentiated...
The tumor is usually extremely cellular, with sheets
of anaplastic cells...individual tumor cells are
small, with little cytoplasm and hyperchromatic nuclei
that are frequently elongated or crescent shaped...
Mitoses
are abundant,
and markers of cellular proliferation, such as
Ki-67, are detected in a high percentage of the cells...
True
rosettes and pseudorosettes...
The tumor has the
potential to express neuronal (neurosecretory granules or
Homer Wright rosettes) and glial
phenotypes...at the edges of the main tumor mass, medulloblastoma cells have a
propensity to form linear chains of cells infiltrating through cerebellar cortex
to aggregate beneath the pia, penetrate the pia, and seed into the subarachnoid
space...
Extension into the
subarachnoid space may elicit a prominent desmoplastic response...
Dissemination through
the CSF is a common complication, presenting as nodular masses elsewhere in the
CNS, including metastases to the caudas equina that are sometimes termed "drop"
metastase b/c of their direct route of dissemination throug the CSF...
The tumor is highly malignant, and the prognosis for untreated patients is
dismal; however, it is an exquisitely
radiosensitive tumor...
Pineal
Parenchymal Tumors
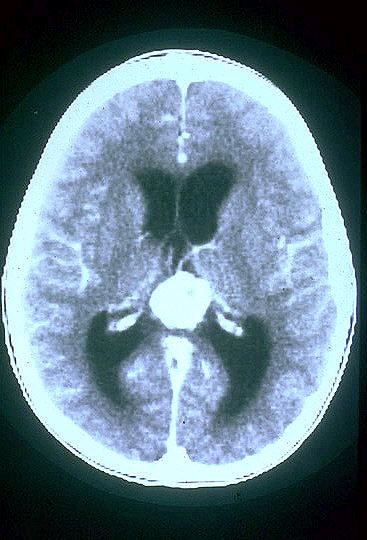
These lesions arise
from the specialized cells of the pineal gland (pineocytes) that have features
of neuronal differentiation...
The tumors range in
histologic appearance from well-differentiated lesions (pineocytomas) with areas
of neuropil, tumor cells with small round nuclei and non evidence of mitoses or
necrosis, to high-grade tumors (pineoblastomas) of densely packed small cells
with necrosis and frequent mitotic figures and little light microscopic evidence
of neuronal differentiation...
The highly aggressive
pineoblastoma commonly spreads throughout the CSF space, is more commonly found
in children, and may occur in patients with retinoblastoma...
Gliomas are also
found in the pineal region, arising from the glial stroma of the gland...
Low grade gliomas at
this site can be difficult to distinguish in a small bipsy from the glial
reaction that can accompany non-neoplastic pineal region cysts...
Pineal
tumors result in parinaud sydnrome: paralysis of upward gaze and
noncommunicating hydrocephalus...
Meningiomas
 Most
often occur in convexities of hemispheres and parasagittal regions...
Most
often occur in convexities of hemispheres and parasagittal regions...
Meningiomas are
predominantly benign tumors of adults, usually attached to the
dura,
that arise from the meningothelial cell of the arachnoid...
Meningiomas may be
found along any of the external surfaces of the brain as well as within the
ventricular system, where they arise from the stroma arachnoid cells of the choroid plexus...
Psammoma bodies and a
whorled pattern
of tumor cells are
somewhat characteristic...
Monosomy
22 is associated with meningioma...
Meningiomas are usually slow-growing lesions that present either with vague
nonlocalizing symptoms or with focal findings referable to compression of
underlying brain...
Meningiomas may cause
overlying, reactive calcifications in the cranium...
Common sites of
involvement include the parasagittal aspect of the brain convexity, dura over
the lateral convexity, wing of the sphenoid, olfactory groove, sella turcica,
and foramen magnum...
They are uncommon in
children and, in general, show a moderate (3:2)
female prodominance, although the ratio becomes 10:1 among patients
with spinal meningiomas...
Lesions are usually
solitary, and their presence at multiple sites, especially in association with
acoustic neuromas or glial tumors,
suggests a diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 2...
The tumors often
express progesterone receptors, and
rapid growth during pregnancy has been reported...
back
to top

![]()